Types of RCDs
Common Types of RCD include, Type AC and Type A, other types include Type B and Type F.
RCDs (Residual Current Device) are available in many types, the RCD type is not to be confused with the overcurrent protective device “curve” type.
RCDs on their own do not offer any kind of overcurrent protection unless it is an RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Over-Current) to BS EN 61009.
The correct RCD type selected all depends on what the RCD is required for, it is the designers responsibility to ensure the correct RCD or RCBO is selected for the job.
BS 7671:2018 regulation 531.3.3 states ‘different types of RCD’s exist, depending on their behavior in presence of DC components and frequencies. The appropriate RCD shall be selected.
RCD Types
The types of Residual Current Devices (RCD’s) include:
- Type AC
- Type A
- Type A-APR
- Type F
- Type EV
- Type B
- Type B+
Each RCD type has a specific set of parameters for which is it suitable.
Type AC RCD
A Type “AC” RCD is for resistive, inductive and capacitive loads.
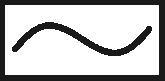
A type AC RCD is only suitable for detecting and tripping on AC sinusoidal wave residual currents.
Note: If any DC current is present then a Type AC RCD may not function – It does not detect DC currents.
Type AC RCD is the most basic of all types of RCD’s and is becoming less and less suitable for todays modern world where most electrical appliances and equipment contain electronic components.
It has been mentioned that type AC RCDs are now only really suitable for immersion heaters / electric panel heaters / tungsten lighting and the like, however this may not be the case if the equipment includes an electronic timer or electronic thermostatic controls or for tungsten lighting if electronic dimming controls are used.
Example Uses for a Type AC RCD
- Electric Shower
- Oven
- Hob
- Immersion Heater
- Tungsten / Halogen Lighting
Type AC RCDs are now banned in some countries.
Type A RCD
A Type “A” RCD is for electronic components with pulsating DC residual currents up to 6mA.

A type A RCD is suitable for detecting and tripping on AC sinusoidal wave residual currents and pulsating DC residual currents up to 6mA.
Note: If a smooth residual DC current greater than 6mA is present then a Type A RCD may not function – It does not detect smooth DC currents.
Example Uses for a Type A RCD
- Induction Hobs
- Lighting with LED drivers
- Lighting with Dimmers
- EV Chargers with less than 6mA smooth residual DC current
Type A variant – Type A-APR : As Type A + High immunity to unwanted tripping (Source: ABB)
Type F RCD
A type “F” RCD is for Frequency controlled equipment.

Note: If a smooth residual DC >10mA is present then the Type F RCD may not function – It does not detect smooth DC currents.
A type F RCD is suitable for detecting on AC sinusoidal wave residual currents and pulsating DC residual currents up to 6mA and high frequency (up to 1kHz) residual currents.
Example Uses for a Type F RCD
- Air con controllers with variable speed drives (VSD)
- Washing machines
- Tumble dryers
- Dishwashers
Some manufactures of white goods such as washing machines, tumble dryers and dishwashers specify the use of a Type F RCD.
Type EV RCD
A type “EV” RCD is suitable for detecting AC and DC residual currents.

In some countries a Type A RCD which also incorporates a RDC-DD is referred to as a Type EV.
The Type EV RCCB has been developed specifically for EV charging systems and can detect AC and DC residual currents in accordance with the requirements of IEC62955. This provides a lower cost option to the Type B RCD, and has been designed specifically for use in Mode 3 and Mode 4 EV charging applications. (Source: westernautomation.com)
Type B RCD
A Type “B” RCD is for variable speed drives (VSD) with smooth DC residual currents.

A type B RCD is suitable for detecting sinusoidal AC, pulsating DC and smooth DC residual currents.
A Type B RCD will detect smooth DC currents and will operate (trip) if the smooth DC current exceeds the trip threshold.
Type B variant – Type B+ : Type B+ devices are sensitive to all residual currents while also being equipped with a special tripping curve that limits the tripping current to maximum 420 mA for frequencies up to 20 kHz. (Source: EATON)
RCD Symbols
The RCD type symbol denotes what type of RCD it is, see the symbols above for each RCD type.
Effects of DC Residual Current on RCDs
The IET have a vary good explanation of the effects of DC residual current on RCDs, below is an excerpt from their Wiring Matters article,
What are the effects of DC residual fault current on RCDs?
To help explain, it might be worth thinking about some older models of earth fault loop impedance testers, which could cause the RCD to operate unintentionally. To prevent this, some types of earth fault loop impedance testers imposed a DC current on the AC test current. This DC current saturated the magnetic core of the RCD preventing it from tripping under the test condition.Where equipment produces an element of residual DC, for example, variable-speed drives is connected to the electrical installation, the DC component can saturate the magnetic core and effectively blind or locks the RCD. This is known as ‘blinding’ and could either prevent the RCD from operating or reduce the sensitivity resulting in a dangerous situation. – Source theiet.org
For further information take a look at the BEAMA Guide to RCD Types and their Applications
Electric Vehicle Chargers and RCDs
RCD protection for EV chargers has its own set of challenges to overcome, the BEMA Guide to RCD Protection of Electric Vehicle Charging Installations is a good reference guide, RCD Selection for EV Chargers.
Variants of RCDs
RCD is a generic term used for a device which incorporates a residual current operated device, but variants exist, such as;
| Type | Full Name | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| RCCB | Residual Current operated Circuit Breaker | Without overcurrent protection, includes, BS EN 61008, BS EN 62423 and BS 4293 |
| RCBO | Residual current operated Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent protection | With overcurrent protection, BS EN 61009. |
| SRCD | Socket-outlet or Spur Residual Current operated Device | With or without overcurrent protection, BS 7288 |
| RDC-DD | Residual Direct Current – Detecting Devices | Mainly used for EV chargers, BS IEC 62955 |
Summery of Types of RCDs
- RCD Type AC = AC sinusoidal wave residual currents only.
- RCD Type A = As Type AC + pulsating DC residual currents up to 6mA.
- RCD Type F = As Type A + high frequency (up to 1kHz) residual currents.
- RCD Type B = As Type F + smooth DC residual currents.
- RCD Type EV = Specifically for mode 3 or mode 4 electric vehicle chargers.
Always refer to the relevant latest manufactures instructions, guidance and technical documents as specifications and requirements may vary and/or change overtime.
Download The App!
Electrical Tools & Reference, full to the brim with tables, charts, forms and calculators.
For further information visit The Electricians App.
Or, get the cloud desktop version →